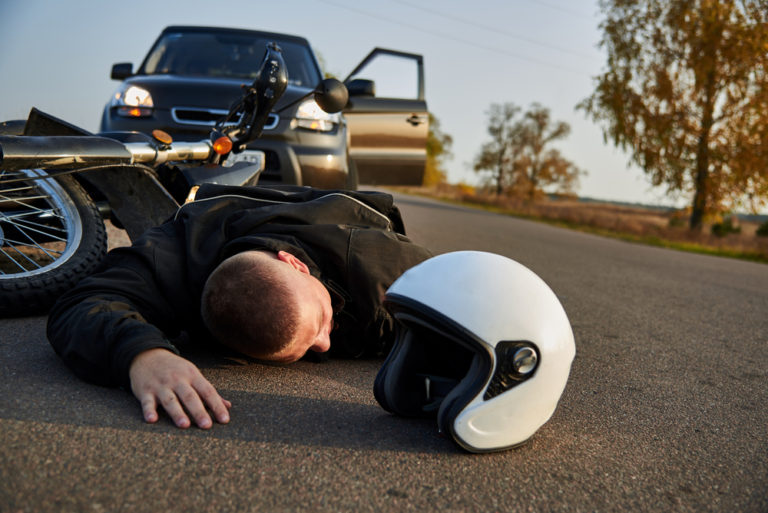
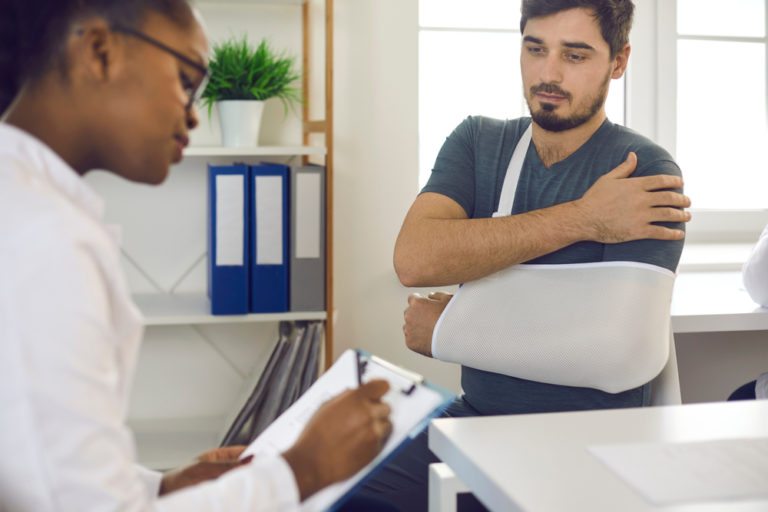
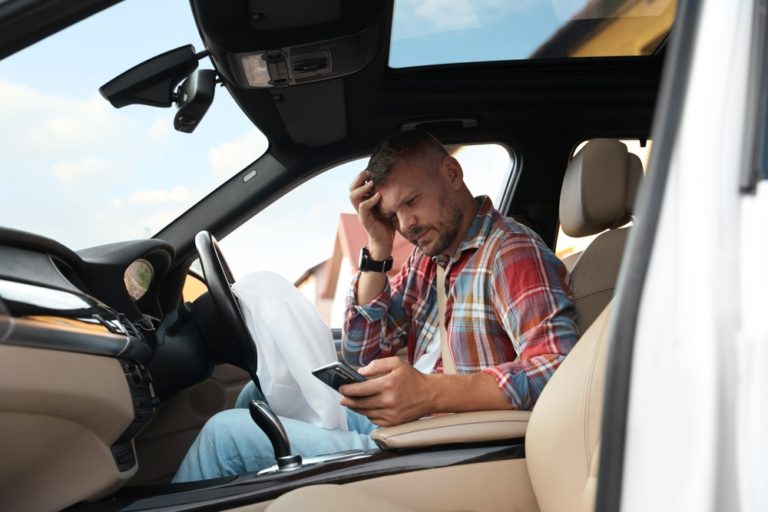
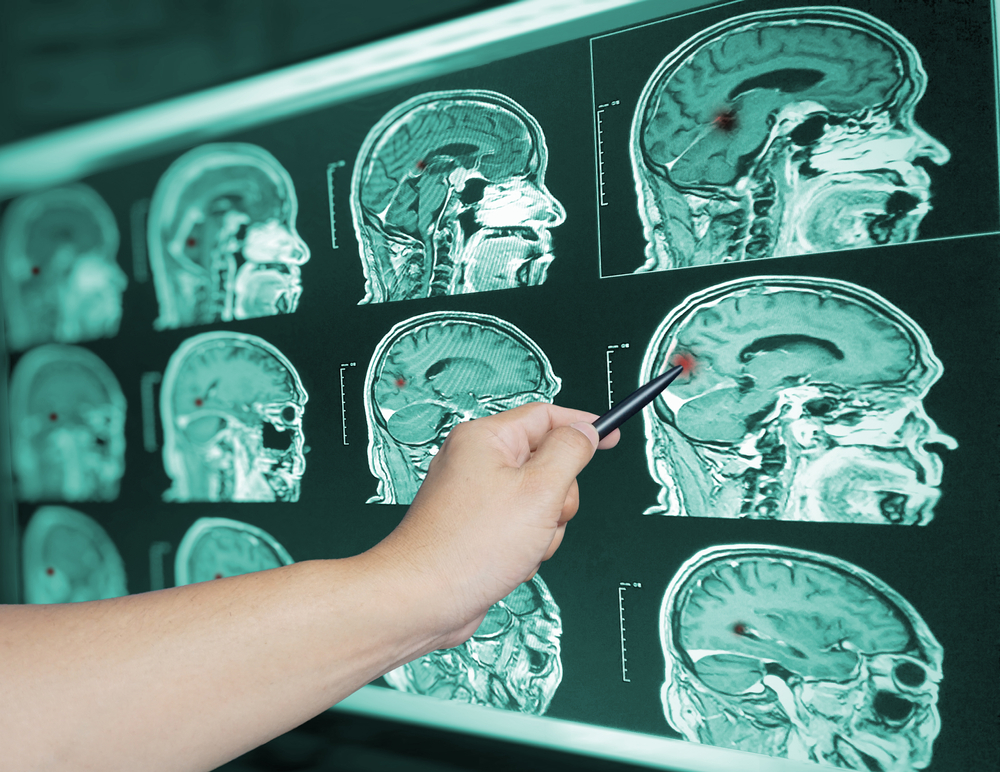
Traumatic Brain Injury is one of the most tragic personal injuries. When severe traumatic brain injuries strike, they can rob victims or precious memories, make them unable to work, and permanently disrupt family life. Some victims lose motor skills and the ability to take care of themselves, resulting in institutionalization.
The victims and their families have rights. When a person or business causes this devastating injury, the law requires them to pay economic and non-economic damages. Olson & Son’s top personal injury litigation team has worked on many traumatic brain injury cases and knows how to win all the damages their clients deserve.
What Is a Traumatic Brain Injury in Kamuela?
Traumatic brain injury describes symptoms and health impacts caused by a violent blow- or jolts to the head or body. For instance, a punch to the head, a jolt during an auto accident, or the impact of a fall represent common causes of traumatic brain injuries. Additionally, objects passing through brain tissue cause traumatic brain injuries, such as bullet or skull fragments.
In the context of personal injury law, we frequently represent clients with traumatic brain injuries due to the following calamities:
- Auto accidents
- Boat accidents
- Aviation accidents
- Falls
- Construction accidents
- Injuries from falling objects
- Sports injuries
- Defective products
- Medical malpractice
- Assaults
- Shootings
Though these events are the most common basis for personal injury lawsuits related to head injuries, it’s essential to understand that a traumatic brain injury caused by any type of negligence by an individual or organization is actionable in Hawaii civil court.
Mild traumatic brain injuries often impact brain cells temporarily and are highly treatable, usually allowing patients to fully recover. For example, the impact of a low-speed auto accident may jolt the brain, causing minor and reversible brain cell impacts.
On the other hand, severe brain injuries, such as blunt force trauma or a high-speed auto crash, lead to severe and life-threatening injuries. The brain may sustain bruising, torn tissues, bleeding, and other damaging and potentially fatal damage.
Some survivors of serious traumatic brain injuries suffer from lifelong disabilities. For instance, former Arizona Congresswoman Gabby Giffords survived an assailant’s bullet to the head. Though she recovered some of her abilities, the injury to the brain could not be fully corrected, leaving her with permanent brain damage.
Similar long-lasting impacts happen to auto accident victims. High-speed crashes impose a force far greater than the human skeleton is designed to withstand.
Traumatic brain injuries result in wide-ranging physical and psychological impacts. Some signs or symptoms appear at the time of the traumatic event but others become apparent days or weeks later. For this reason, we always recommend seeking prompt medical treatment after a head injury and to attend all follow-up medical visits.
From a legal standpoint, failure to seek medical care immediately after the event or attend subsequent appointments can jeopardize your case. For instance, imagine you fell and took a blow to the head but figured you were okay and wanted to avoid a costly emergency room visit. Then, over the coming days and weeks, you develop headaches, fatigue, and memory loss that indicate traumatic brain injury. You then visit a doctor, who determines you have a traumatic brain injury.
In court, the defense could dispute that the injury resulted from the alleged fall. It could maintain that you must have suffered the injury during a separate incident for which their client has no liability. Depending on the overall strength of your case, they could win this argument.
Symptoms of Mild Traumatic Brain Injury in Kamuela
Mild traumatic brain injury symptoms include physical, sensory, and mental varieties:
Physical Symptoms
- Headache
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Fatigue
- Speech difficulties
- Dizziness
- Loss of balance
Sensory Symptoms:
- Blurred vision
- Ringing in the ears
- Strange taste in the mouth
- Loss of sense of smell l
- Light sensitivity
- Sound sensitivity
Mental Symptoms
- Loss of consciousness for a few seconds to several minutes
- Feeling dazed, confused, or disoriented
- Memory problems
- Concentration difficulties
- Mood changes
- Mood swings
- Depression
- Anxiety
- Insomnia
- Oversleeping
Symptoms of Moderate to Severe Traumatic Brain Injuries in Kamuela
Moderate to severe traumatic brain injuries often include some signs and symptoms of mild traumatic brain injury and the more serious symptoms below, which begin hours or days after the traumatic event:
Physical Symptoms
- Loss of consciousness for several minutes to hours
- Persistent headache
- Worsening headache
- Repeated vomiting
- Persistent nausea
- Convulsions
- Seizures
- Dilation of one or both pupils
- Clear fluids leaking from the nose or ears
- Inability to awaken
- Weakness or numbness in the extremities
- Loss of coordination
Cognitive or Mental Symptoms
- Extreme confusion
- Agitation
- Combativeness
- Unusual behavior
- Slurred speech
- Coma
Children’s Symptoms
Infants and young children require extensive observation after a head injury because they may be unable to express the symptoms they experience. A medical evaluation is always recommended. Children with traumatic brain injury may display the following signs:
- Change in eating or nursing habits
- Unusual irritability
- Persistent crying
- Inconsolability
- Unusually short attention span
- Insomnia
- Oversleeping
- Inability to wake
- Seizures
- Depressed mood
- Drowsiness
- Loss of interest in favorite toys or activities
Proving Liability for Traumatic Brain Injury in a Personal Injury Case
People who suffer a traumatic brain injury because of another individual’s or organization’s negligence or intentional action have a claim for damages. The key to winning resides in the ability to prove negligence or intentional action that resulted in the injury. When preparing a personal injury case, attorneys seek evidence that demonstrates the four key elements they must demonstrate in court:
- The defendant(s) has a duty of care
- The defendant(s) breached that duty of care
- The defendant(s) breach caused the plaintiff harm
- The harm resulted in the damages claimed
The plaintiff must prove each of these elements by a preponderance of the evidence. A preponderance of the evidence means more likely than not. So, in the case of a traumatic brain injury, the plaintiff must prove to a jury that the defendant(s) breach of a duty of care more than likely caused injury.
Insurance company attorneys look for weaknesses in the evidence of the four elements to create a defense. For instance, they may argue that the defendant’s breach of duty was not the cause of the injury. If the defense has no evidence that the breach caused the harm, the case fails.
Proving the Duty of Care
Often, proving duty of care is simply because the law presumes the duty. For example, all drivers have a duty of care while operating a motor vehicle. A defendant in an auto accident claim could dispute that he breached the duty of care, but he won’t get anywhere arguing that he has no duty of care.
Another example of a presumed duty of care is premises liability. The law presumes that the owner of a property has a duty of care, so if the plaintiff sues after falling, the defense could claim there was no breach but not that no duty of care existed.
Some exceptions exist. For example, a property owner could argue he has no duty of care against trespassers or people on the property illegally. How can he possibly exercise a duty of care toward people that are misusing his property or engaged in a crime?
Proving a Breach of the Duty of Care
Because establishing a duty of care is usually straightforward, cases tend to hinge on proving that the defendant breached the duty of care. For example, just because a property owner has a duty of care and the plaintiff sustained injury on the premises does not necessarily mean that the defendant breached the duty.
For instance, a person may have fallen at a grocery store after tripping on an untied shoelace. The fall happened because of the injury victim’s own mistake, not because the business failed in its duty of care.
On the other hand, if the store left a loose tile in the path of customers, causing a fall with traumatic brain injury, then the business was negligent.
Proving the Breach Caused Harm in Kamuela
A breach of the duty of care alone cannot win a personal injury case. The breach must have caused actual harm to the plaintiff. A great example of this is a person who slips on a wet floor at a business. Was the individual harmed? If there is no harm, there is no liability in personal injury law.
For this reason, it’s always important to seek medical attention promptly. An exam generates the medical records needed to show that harm resulted from the incident. Without these records, the defense could argue that the event caused no injury and that the damages alleged had another cause.
Proving the Harm Resulted From the Damages Claimed
Finally, the plaintiff must show that the harm caused the damages claimed. In a traumatic brain injury case, medical records and corresponding bills serve to prove that these expenses are related to the harm in question. Similarly, documents showing lost income due to being in the hospital or declared unable to work due to the injury help the plaintiff recover related lost wages.
Proving that general damages resulted from the said harm is less straightforward. General damages include non-economic harms, such as pain and suffering, emotional distress, and loss of enjoyment of life. The defense may question whether the pain or emotional distress experienced by the victim was really caused by the accident. Pain and distress have many sources.
To prove this element, personal injury attorneys use medical records, witness testimony, the victim’s testimony, and other proofs. For example, after a traumatic brain injury, many attorneys will recommend the victim or a family member keep a diary detailing the struggles experienced by the victim. This record provides solid evidence of the damages that resulted from the said harm.
No one wants to imagine themselves or a loved one experiencing a traumatic brain injury. Though mild cases may result in a full recovery, many victims never regain their full abilities. In the worst situations, brain damage causes permanent memory loss, cognitive disability, loss of motor skills, and even devastating personality and behavioral changes.
Talk to an Attorney Right Away in Kamuela
If you or a loved one have suffered a traumatic brain injury because of another person or organization’s negligence or actions, you have the right to compensation. Contact Olson & Sons for a free consultation.
Related Content: What are Special Damages Personal Injury in Kamuela?